Overview
Seller Manager Lite is a desktop application, written in Java, for managing phone sales. The user interacts with it using a Command Line Interface, and views data using a Graphical User Interface, where data is displayed in the form of lists. As the database was designed specifically to support phone sales, database objects such as Customers, Phones and Orders have predefined relationships between them.
Summary of contributions
-
Major enhancement: Added the ability to autocomplete commands.
-
What it does: allows the user to input commands with ease. As the user types into the command line, suggestions will be shown.
-
Justification: This feature improves the product significantly because a user does not need to remember what commands are available or constantly refer to the user guide. It also allows the user to determine if he is entering duplicated data in real time, instead of waiting for feedback after entering the command.
-
Highlights: This enhancement supports all existing commands of varying formats and was designed to be easily extensible to commands added in future. The autocomplete system is contextually aware, by suggesting values catered to each command and prefix specifically. The possible values will also automatically update according to changes in the database.
-
Credits: UI code for displaying a dropdown menu was inspired by this StackOverflow post: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/36861056/javafx-textfield-auto-suggestions
-
-
Minor enhancement: Refactored the Model to use generic DataBook and UniqueList that store Identifiable objects.
-
Minor enhancement: Implemented the Phone class.
-
Minor enhancement: Implemented "cascading" effects for edit and delete for database objects.
-
Code contributed:
-
Other contributions:
-
Project management:
-
Released
v1.2on GitHub
-
-
Enhancements to existing features:
-
Removed unwanted AB3 code related to Person
-
-
Community:
-
PRs reviewed (with non-trivial review comments): #141, #83, #106
-
Reported bugs and suggestions for other teams in the class ( ExerHealth #203, ExerHealth #204, ExerHealth #205, ExerHealth #206, ExerHealth #209, ExerHealth #210, ExerHealth #219, ExerHealth #220, ExerHealth #221, ExerHealth #222, ExerHealth #223, ExerHealth #226, ExerHealth #227 )
-
-
Contributions to the User Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the User Guide. They showcase my ability to write documentation targeting end-users. |
Autocomplete
As you type into the command line, suggestions will appear.
A maximum of 8 suggestions will appear in a dropdown menu, sorted by their degree of similarity to the entered text.
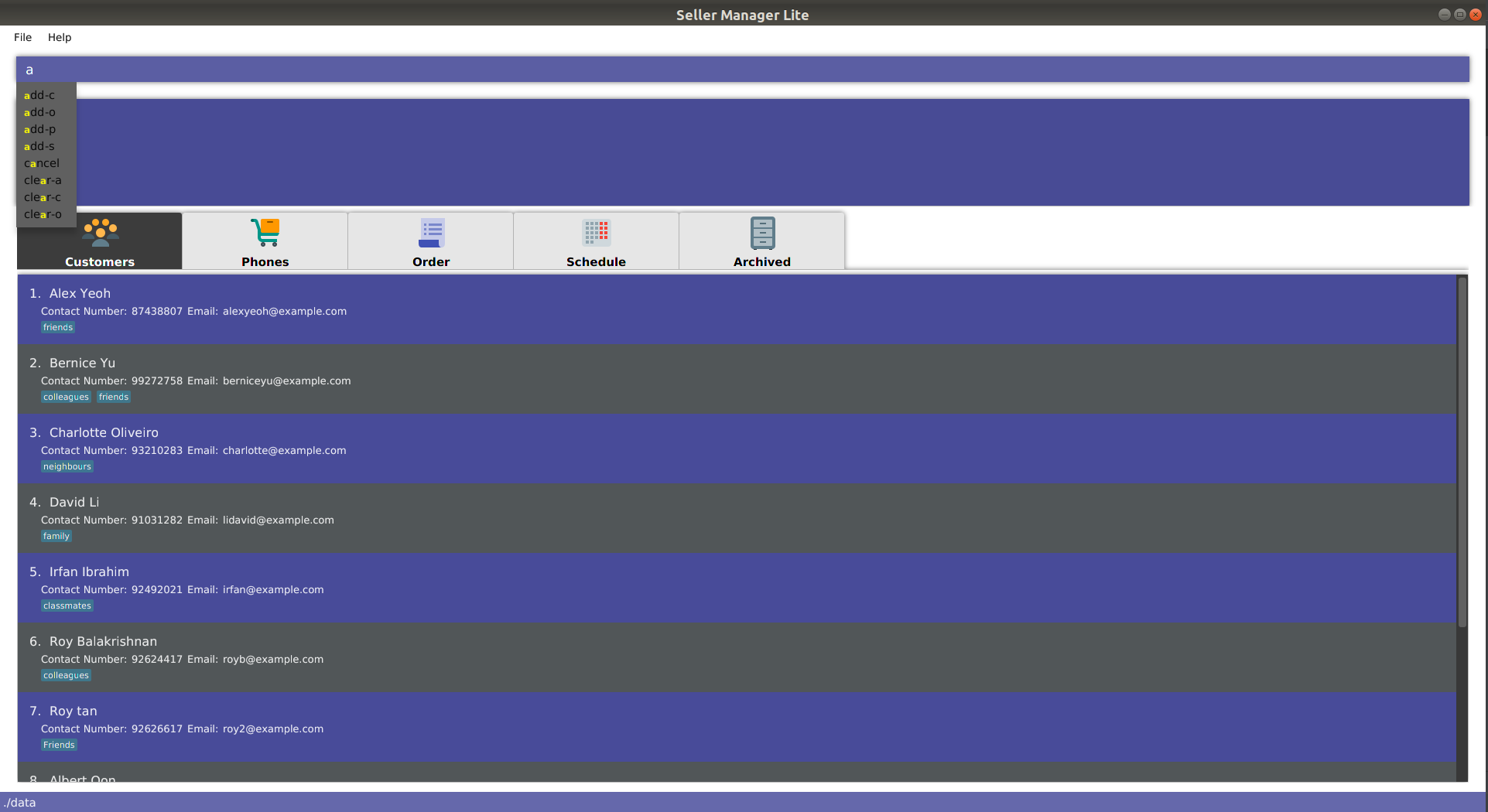
| Suggestions in Cyan mean that the entire word is suggested. |
| Suggestions in Yellow mean that the word is partially matched. |
| The system may lag and not work if you are typing too fast. |
| The system is case-sensitive. |
add
-
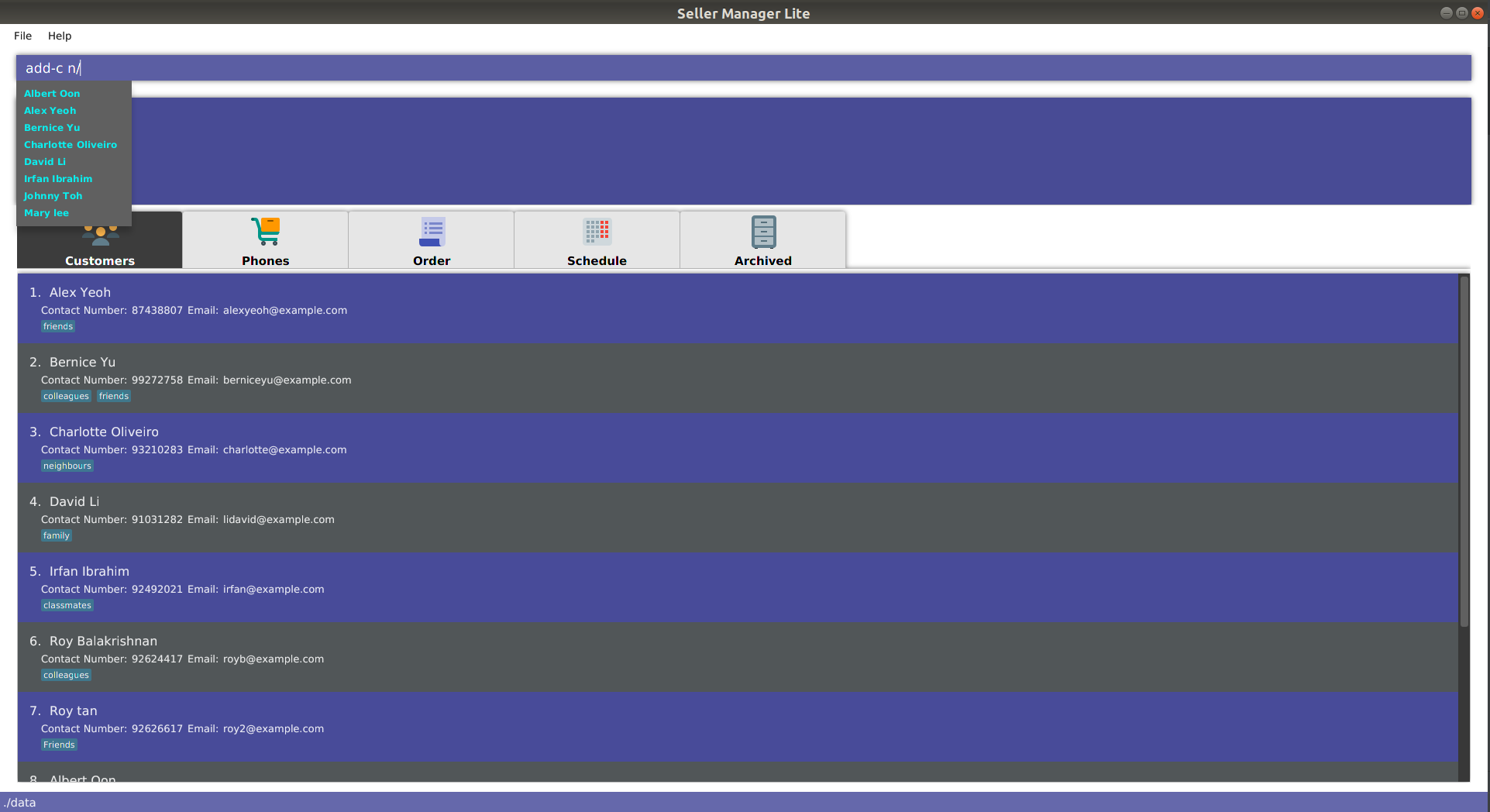
When you enter
add-cfollowed by a space, the system will suggest a list of prefixes you can enter, such asn/. -
When you enter
add-c n/, the system will suggest a list of names that belong to existing customers. This is helpful in checking if the data you are entering is duplicated. -
The list of data that is suggested depends on the prefix that is last entered. For instance, if the last entered prefix was
e/, it would instead suggest a list of existing emails.
delete
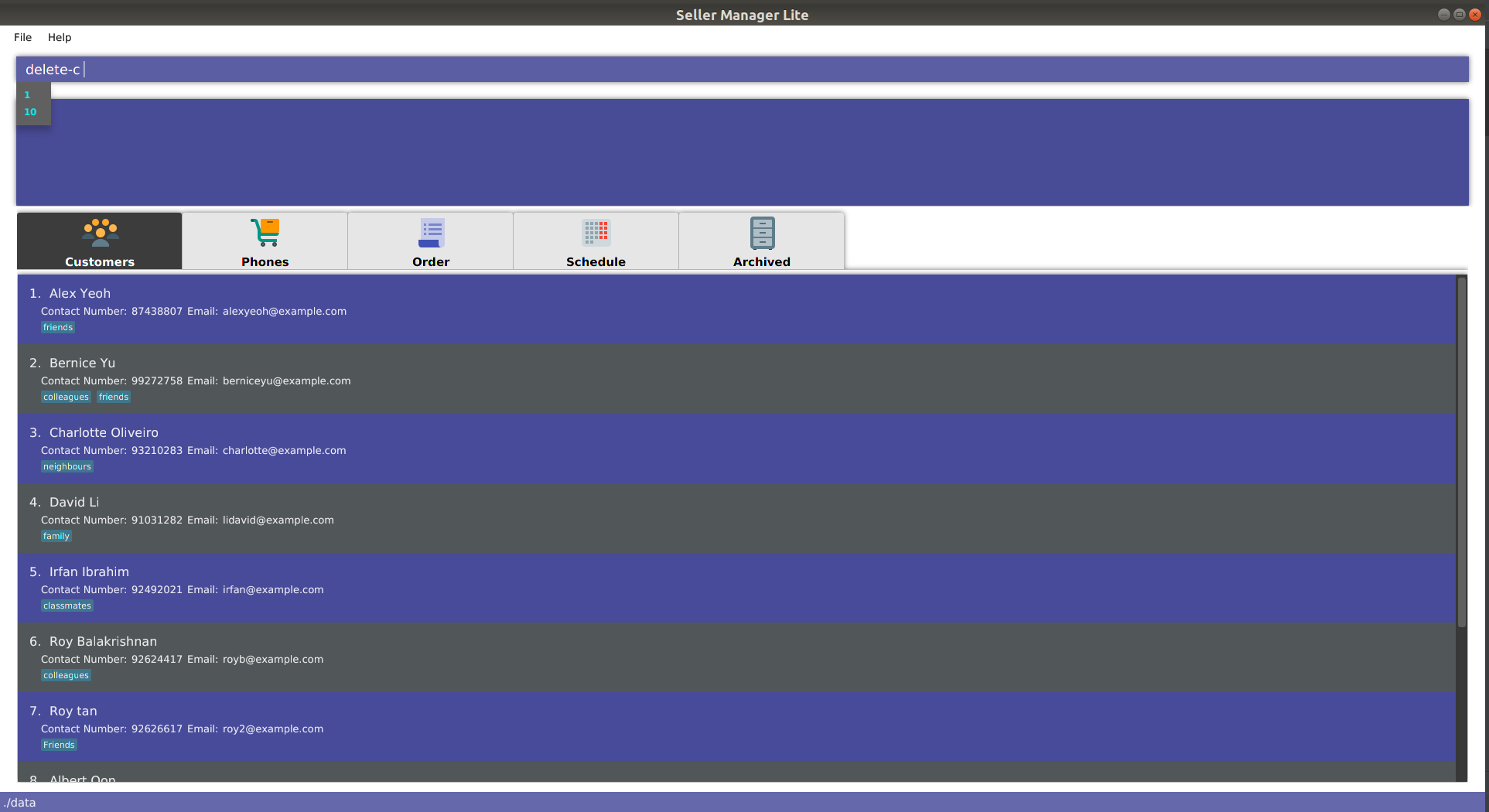
-
For commands such as
delete-cwhich take only a single index and no additional arguments, the system will suggest two numbers:1andN, whereNis the largest valid index that can be entered. In this case,Ncorresponds to the number of customers displayed on the customer panel.
edit
-
When you enter
edit-cfollowed by a space, the system will suggest two numbers:1andN, whereNis the largest valid index that can be entered. -
When you enter
edit-c 1followed by a space, the system will suggest a list of prefixes you can enter, such asn/,c/,e/. -
When you enter
edit-c 1 c/, the system will suggest a list of contact numbers that belong to existing customers. This is helpful in checking if the data you are editing to is duplicated. -
The list of suggestions depends on the prefix that is last entered. If the last entered prefix was
i/, it would instead suggest a list of existing identity numbers.
find
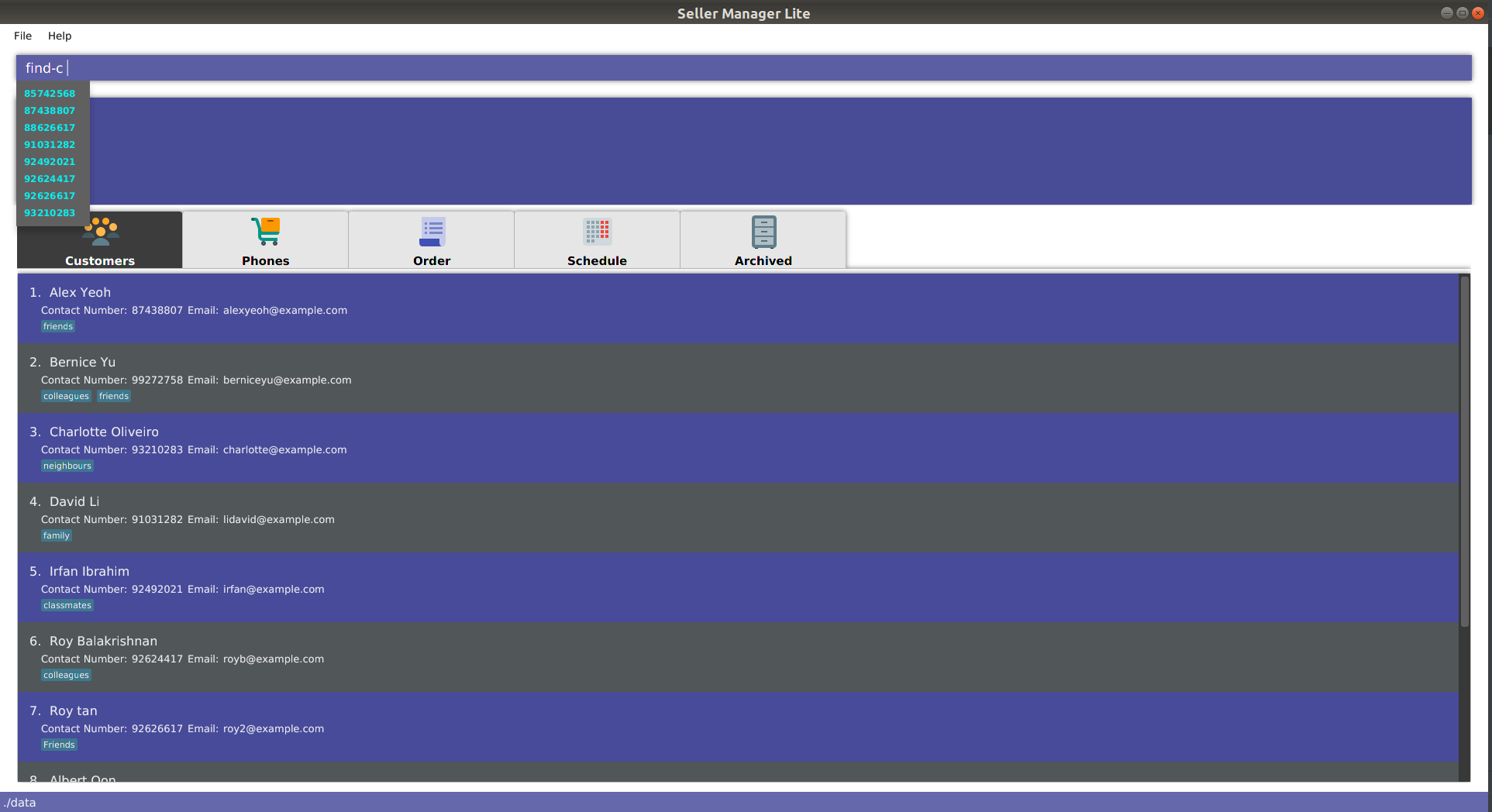
-
When you enter
find-cfollowed by a space, the system will suggest values from every attribute of every customer in the database.
switch
-
For simple commands such as
switch-c, the system will suggest the command word and nothing else.
schedule
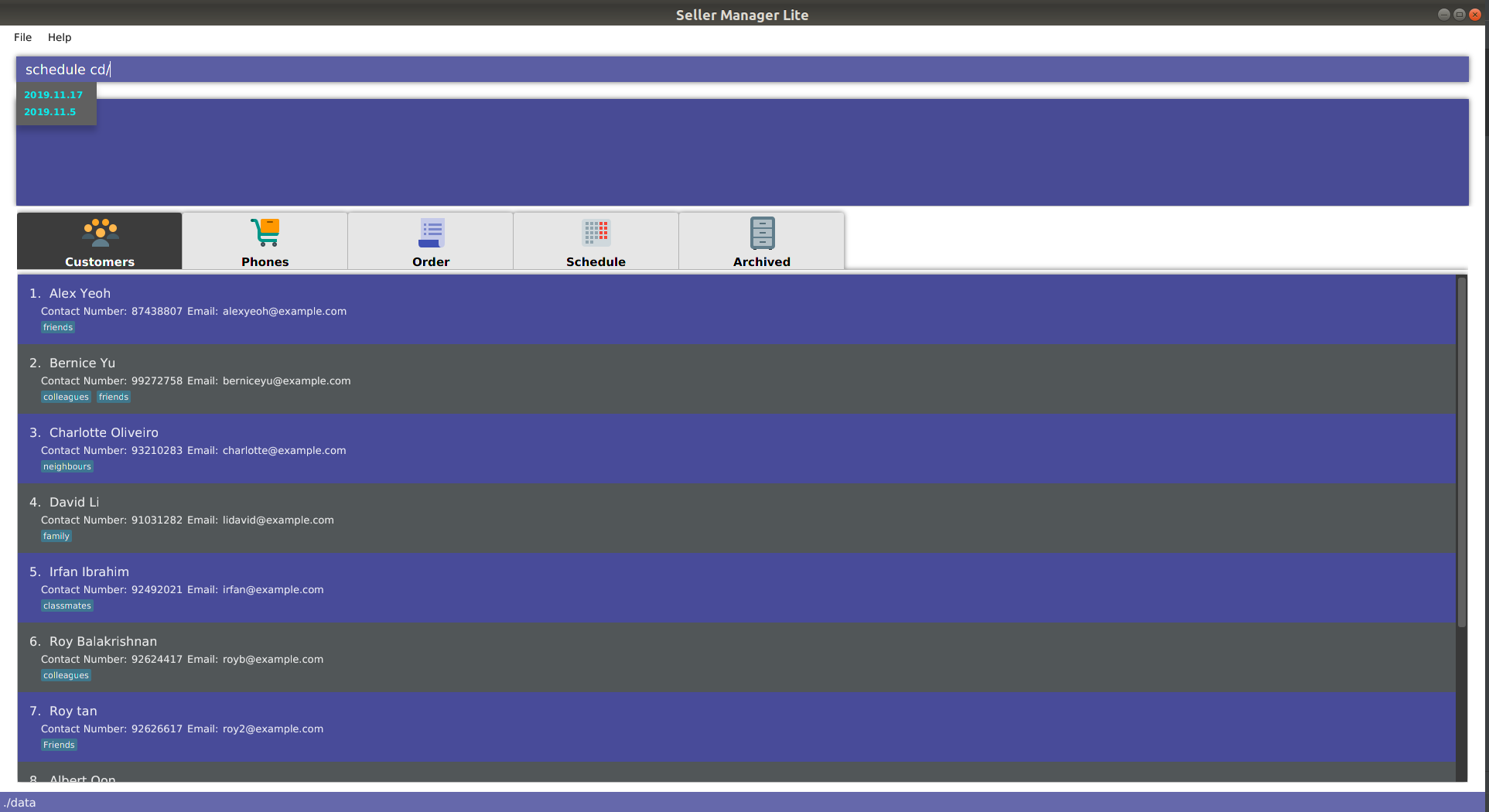
-
When you enter
schedulefollowed by a space, the system will suggest dates that already have orders scheduled on them. This is helpful in checking for duplicates.
Autocomplete integrated with command history [coming in v2.0]
This extension of the autocomplete feature is to allow users to receive suggestions based on past inputs.
Alias [coming in v2.0]
This feature is to allow users to define customized command words to
simplify long commands. For example, generate-s s/profit can be
simplified to gp.
Contributions to the Developer Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the Developer Guide. They showcase my ability to write technical documentation and the technical depth of my contributions to the project. |
Autocomplete feature
This feature is visible in the UI as a dropdown menu when the user types into the command box.

Current Implementation
How the UI works
The command box uses a custom AutoCompleteTextField which extends from JavaFX’s
TextField. It stores a reference to a SortedSet of strings. When the input is
changed, it automatically compares the input with this set of suggestions. If any
suggestion matches some region of the input, it will be further compared with other
suggestions to determine which suggestion is more similar to the input. The degree of
similarity is determined by the index of the first character of the matching region.

The smaller the index, the more similar the suggestion is.
In order to customize the suggestions to fit different inputs, the CommandBox
attaches a listener to the AutoCompleteTextField. When the text is changed, the
CommandBox will extract the entered text and query the LogicManager for a set
of suggestions. This query process will be explained below.
Underlying data structures
This feature was designed to display values that are currently in the Model.
For example, the input text add-c n/ would display a list of CustomerName
that already exists in the Customer DataBook.
Directed Graph
In order to achieve this, one of the data structures used is a directed Graph
implemented as a list of Edge, each storing references to a source and destination
Node. Each Node then stores a reference to a List in a DataBook.
These were the design considerations:
-
Enforcement of artificial prefix order: By storing prefixes as edge weights, it is possible to enforce an artificial order. First, initialise a pointer to a starting
Node. Then for each prefix encountered in the input, attempt to traverse an outgoingEdgefrom thisNodeby matching the prefix with the edge weight. This way, if the prefix is out of order, later prefixes will be inaccessible. -
Dynamically updated: By storing references to a set of values that can be backed by
ObservableListin theModel, whenever the user alters any data, it will automatically be reflected in the displayed values. -
Supports optional arguments: By storing the possible prefixes as edge weights, it is possible to represent an optional argument by having an edge to the
Nodecontaining its values, as well as an edge to the nextNode. -
Infinite structure: By having a
TagNodestore a reference to itself, it is possible to endlessly displayt/as a possible prefix at the end of the input text, which is consistent with the unlimited number ofTagaCustomercan hold.
Wrapper for a pointer
The idea here is similar to the above. It can be thought of as a singular
Node. This data structure is used for simple commands which require only
one argument. As there is no need to enforce any order or support an
infinite structure, a Graph would be overkill.
Specifics
This is an example sequence diagram for add-c n/.
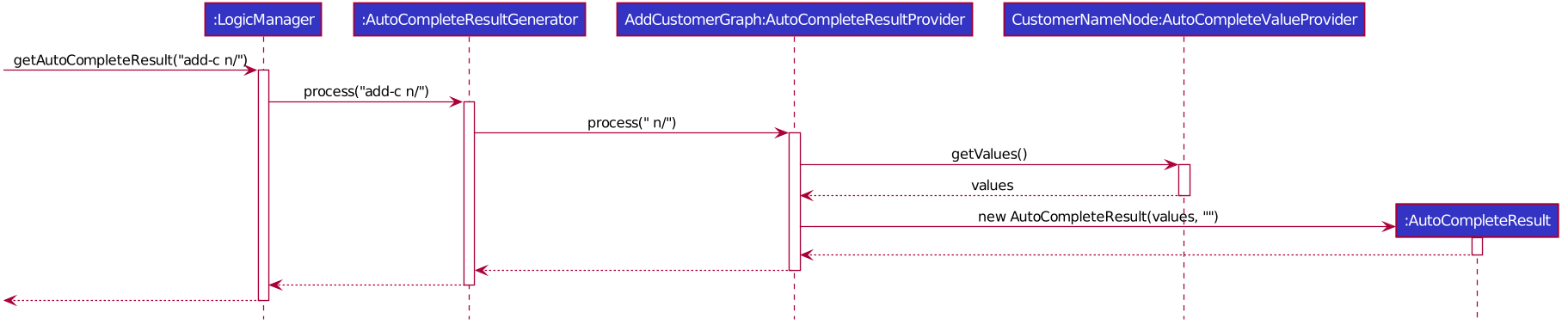
When the UI queries the LogicManager for suggestions, an AutoCompleteResult
is returned, which contains a SortedSet of strings and a separate string to match
with these suggestions.
In order to generate this AutoCompleteResult, the LogicManager requests
a AutoCompleteResultGenerator to process the input.
AutoCompleteResultGenerator contains references to AutoCompleteResultProvider
which have the ability to return AutoCompleteResult.
An example of a AutoCompleteResultProvider would be AddCustomerGraph, which
does the heavy lifting in terms of processing the input string and collating values
from AutoCompleteValueProvider in the form of AutoCompleteNode.
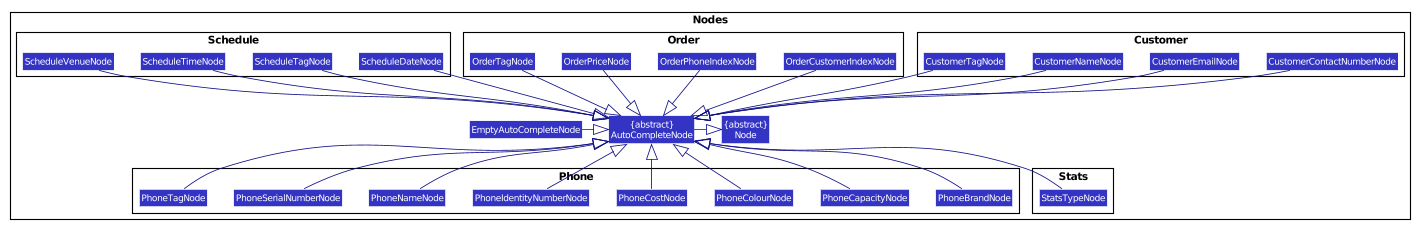
For clarity, here are some class diagrams for the AutoComplete package.
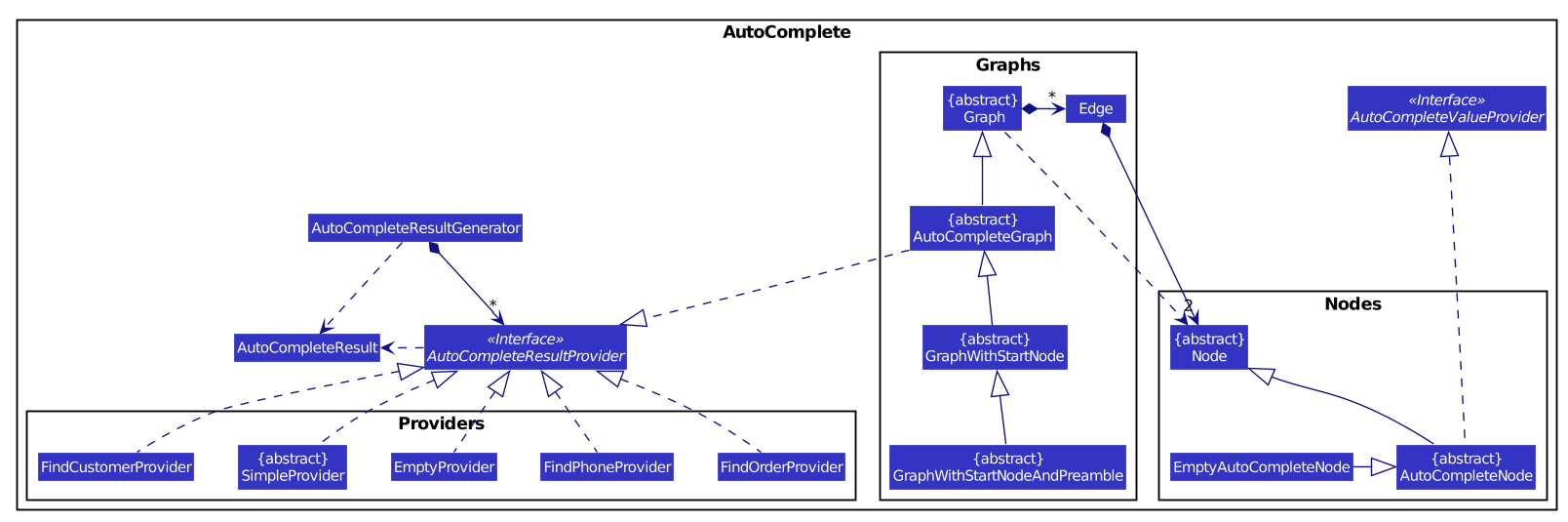
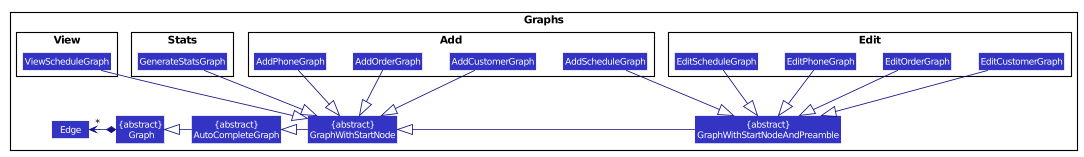
Alternative Designs
An alternative design would be to integrate the system with existing Parser
by making use of ArgumentTokenizer and ArgumentMultimap.